Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2020-039, 59 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of high-resolution imaging camera for alpha dust" conducted in FY2019. We have developed an imaging camera with a position resolution of less than approximately 10  m to monitor alpha dust in the nuclear plant during the decommissioning process, because the operators avoid to drawing in such dusts. Moreover, we have developed real-time monitor system with optical fiber and scintillator under high dose-rate condition.
m to monitor alpha dust in the nuclear plant during the decommissioning process, because the operators avoid to drawing in such dusts. Moreover, we have developed real-time monitor system with optical fiber and scintillator under high dose-rate condition.
Kobayashi, Takuya; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kamidaira, Yuki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(11), p.635 - 639, 2020/11
, 62(11), p.635 - 639, 2020/11
It is important to predict the dispersion of radioactive materials released into the ocean due to nuclear accidents in the surrounding ocean of the east Asian countries. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency developed a Short-Term Emergency Assessment system of Marine Environmental Radioactivity (STEAMER) based on an oceanic dispersion model. STEAMER quickly predicts the oceanic dispersion of radioactive materials in the surrounding ocean of the east Asian countries using the online prediction data of oceanic condition. We validated the predictability of the oceanic dispersion and demonstrated the improvement of the predictability using an ensemble prediction method. Moreover, we developed a high resolution model in the coastal region using a Regional Ocean Modeling System (ROMS).
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2019-038, 57 Pages, 2020/03
JAEA/CLADS, had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Imaging System with Ultra-high Spatial Resolution Aiming to Detect Alpha-dust". In the present study, we have developed a prototype of a system aiming to elucidate the behavior of alpha-dust generated at the time of debris retrieval. In this system, alpha-ray is first converted to visible light by novel scintillator. Then, imaging with ultra-high resolution will be possible using a lens and an Si-semiconductor camera (CMOS camera). Also, it will be possible to identify the species of alpha-ray emitting nuclides by unfolding of the spectra. The demonstration tests of the system will be conducted for dust samplers at the Plutonium Fuel Development Center, JAEA. In the development of the present system, it is important to use scintillator whose emission wavelength is sensitive to the CMOS camera as well as high emission scintillator. Considering these conditions, the key technology will be the improvement of the purity of crystals and optimization of the shapes of the materials including powers.
Nakayama, Hiromasa; Nagai, Haruyasu
JAEA-Data/Code 2015-026, 37 Pages, 2016/03
We developed LOcal-scale High-resolution atmospheric DIspersion Model using Large-Eddy Simulation (LOHDIM-LES). This dispersion model is designed based on LES which is effective to reproduce unsteady behaviors of turbulent flows and plume dispersion. The basic equations are the continuity equation, the Navier-Stokes equation, and the scalar conservation equation. Buildings and local terrain variability are resolved by high-resolution grids with of a few meters and these turbulent effects are represented by immersed boundary method. In simulating atmospheric turbulence, boundary layer flows are generated by a recycling turbulent inflow technique in a driver region set up at the upstream of the main analysis region. This turbulent inflow data are imposed at the inlet of the main analysis region. By this approach, the LOHDIM-LES can provide detailed information on wind velocities and plume concentration in the investigated area.
 La
La B
B revealed by high-resolution X-ray diffraction
revealed by high-resolution X-ray diffractionInami, Toshiya; Michimura, Shinji*; Hayashi, Yuya*; Matsumura, Takeshi*; Sera, Masafumi*; Iga, Fumitoshi*
Physical Review B, 90(4), p.041108_1 - 041108_5, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:38.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We carried out a high-resolution X-ray diffraction experiment on Ce La
La B
B . This compound exhibits antiferro-octupole order (AFO) below
. This compound exhibits antiferro-octupole order (AFO) below 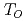 = 1.4 K, and it is theoretically suggested that ferroquadrupole moments and a resultant rhombohedral deformation are induced in the AFO phase. We observe the splitting of Bragg reflections below
= 1.4 K, and it is theoretically suggested that ferroquadrupole moments and a resultant rhombohedral deformation are induced in the AFO phase. We observe the splitting of Bragg reflections below 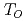 and find that the unit cell is rhombohedral with the elongated [111] axis. We also precisely evaluate the magnitude of the induced quadrupole moments from the obtained shear strain and find that the quadrupole moments are not reduced in the AFO phase.
and find that the unit cell is rhombohedral with the elongated [111] axis. We also precisely evaluate the magnitude of the induced quadrupole moments from the obtained shear strain and find that the quadrupole moments are not reduced in the AFO phase.
Agematsu, Takashi; Hanaya, Hiroaki
JAEA-Review 2005-001, TIARA Annual Report 2004, p.355 - 357, 2006/01
We examined a combination of Gaf-chromic film dosimeter HD-810 and an image scanner for a personal computer as two-dimensional densitometer which is cheap, easy to use and allows speedy measurement with high spatial resolution. Linearity of dose response was mesured with RGB component up to 500Gy. The cause of low uniformity in ion beam fluense distribution at the JAERI AVF cyclotron raster beam scanning system was clarified by this method, which was a very sharp concentration of fluence in a beam spot.
 Sb
Sb Te
Te thin films; An X-ray absorption study
thin films; An X-ray absorption studyFons, P.*; Kolobov, A.*; Tominaga, Junji*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 238(1-4), p.160 - 162, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.08(Instruments & Instrumentation)Super-resolution (SR) media offer up to a factor of ten increase in areal storage density over conventional DVD media. Although SR has been realized, there is a strong need for a deeper understanding of structural and electronic changes in Ge Sb
Sb Te
Te (GST), a principal optical memory component, with external perturbations. Recording of SR disks leads to the formation of gas-phase bubbles that in turn lead to the development of large stresses on the underlying GST layer. In this paper we report on XAFS of nominally hydrostatic (0-10 GPa) compressive stress-induced structural changes of the metastable crystalline phase of GST. An analysis showed that the initial splitting of Ge Te bond lengths of the room-temperature distorted rocksalt structure decreased to a small but finite splitting for
(GST), a principal optical memory component, with external perturbations. Recording of SR disks leads to the formation of gas-phase bubbles that in turn lead to the development of large stresses on the underlying GST layer. In this paper we report on XAFS of nominally hydrostatic (0-10 GPa) compressive stress-induced structural changes of the metastable crystalline phase of GST. An analysis showed that the initial splitting of Ge Te bond lengths of the room-temperature distorted rocksalt structure decreased to a small but finite splitting for 
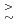 6 GPa. The implications of this upon the proposed ferroelectric catastrophe super-RENS readout mechanism are discussed.
6 GPa. The implications of this upon the proposed ferroelectric catastrophe super-RENS readout mechanism are discussed.
 He for neutron detection
He for neutron detectionNakamura, Tatsuya; Masaoka, Sei; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Tanaka, Hiroki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 539(1-2), p.363 - 371, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)We evaluated the neutron-detection performance of a capillary plate under high-pressure helium-3 in terms of the gas gain and the distribution of pulse heights, with the aim of using the device as a neutron detector and a gas preamplification device. The capillary plate exhibited a gas gain of more than 1000 up to a gas pressure of 6 atm with a 5% mixture of ethane, confirming an adequate gas gain as a neutron detector. It was also found that the rise times of the signal pulses were correlated with the range and the emission angle of the secondary particles, protons and tritons, thereby providing useful information for developing a system with position-sensitive readouts with a high spatial resolution and a low background.
 LiF scintillating and MSGC neutron detectors in JAERI
LiF scintillating and MSGC neutron detectors in JAERINakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri, Masaki; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Tanaka, Hiroki; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Hamon, 15(1), p.67 - 73, 2005/01
Development of scintillating and gaseous neutron detectors in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute is briefly described. In this paper, the performances of the developed 2-d neutron detectors, concerning ZnS/ LiF scintillating detectors with wavelength shifting fiber read-out and micro-strip gas chambers with individual read-out, are presented.
LiF scintillating detectors with wavelength shifting fiber read-out and micro-strip gas chambers with individual read-out, are presented.
 64 channel high-position resolution neutron imaging detector
64 channel high-position resolution neutron imaging detectorSakasai, Kaoru; Katagiri, Masaki; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Rhodes, N.*; Schoonveld, E.*
JAERI-Research 2004-020, 19 Pages, 2004/12
no abstracts in English
 resolution
resolutionChatake, Toshiyuki*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Tsyba, I.*; Bau, R.*; Jenney, F. E. Jr.*; Adams, M. W. W.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 60(8), p.1364 - 1373, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:88.89(Biochemical Research Methods)A neutron diffraction study has been carried out at 1.6  resolution on a mutant rubredoxin from
resolution on a mutant rubredoxin from 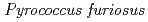 using the BIX-3 single-crystal diffractometer at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. In order to study the unusual thermostability of rubredoxin from
using the BIX-3 single-crystal diffractometer at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. In order to study the unusual thermostability of rubredoxin from 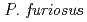 , the hydrogen-bonding patterns were compared between the native and a 'triple-mutant' variant where three residues were changed so that they are identical to those in a mesophilic rubredoxin. In the present study, some minor changes were found between the wild-type and mutant proteins in the hydrogen-bonding patterns of the Trp3/Tyr3 region. The H/D-exchange ratios in the protein were also studied. The results suggest that the backbone amide bonds near the four Cys residues of the FeS
, the hydrogen-bonding patterns were compared between the native and a 'triple-mutant' variant where three residues were changed so that they are identical to those in a mesophilic rubredoxin. In the present study, some minor changes were found between the wild-type and mutant proteins in the hydrogen-bonding patterns of the Trp3/Tyr3 region. The H/D-exchange ratios in the protein were also studied. The results suggest that the backbone amide bonds near the four Cys residues of the FeS redox center are most resistant to H/D exchange. In addition, the 1.6
redox center are most resistant to H/D exchange. In addition, the 1.6  resolution of the present neutron structure determination has revealed a more detailed picture than previously available of some portions of the water structure, including ordered and disordered O-D bonds.
resolution of the present neutron structure determination has revealed a more detailed picture than previously available of some portions of the water structure, including ordered and disordered O-D bonds.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Masaoka, Sei; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 529(1-3), p.336 - 341, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.89(Instruments & Instrumentation)A microstrip gas chamber (MSGC) with a capability of track discrimination for neutron detection was developed whilst ensuring the stability of the MSGC and fulfilling the specifications required for detectors using in high-flux reactors and high-intensity pulsed-neutron sources. The developed two-dimensional detector system comprises a MSGC with individual signal channel read-outs and a new instrument system with a capability of secondary-particle discrimination (InSPaD). The InSPaD identifies the particles -proton and triton- created in the nuclear reaction 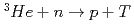 by a simple, fast and cost-effective method using the difference in the track length, and it enables a small amount of heavy gas such as
by a simple, fast and cost-effective method using the difference in the track length, and it enables a small amount of heavy gas such as 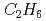 with helium-3 to be used as the filling gas whilst achieving a high spatial resolution.
with helium-3 to be used as the filling gas whilst achieving a high spatial resolution.
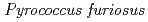 by BIX-3, a single-crystal diffractometer for biomacromolecules
by BIX-3, a single-crystal diffractometer for biomacromoleculesKurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Adams, M. W. W.*; Jenney, F. E. Jr.*; Moiseeva, N.*; Bau, R.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(31), p.11215 - 11220, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:61.13(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The structure of a rubredoxin (Rd) from  , an organism that grows optimally at 100
, an organism that grows optimally at 100  C, was determined using the neutron single-crystal diffractometer for biological macromolecules (BIX-3) at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. Data were collected at room temperature up to a resolution of 1.5
C, was determined using the neutron single-crystal diffractometer for biological macromolecules (BIX-3) at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. Data were collected at room temperature up to a resolution of 1.5  , and the completeness of the data set was 81.9 %. The model contains 306 H atoms and 50 D atoms. A total of 37 hydration water molecules were identified. The model has been refined to final agreement factors of
, and the completeness of the data set was 81.9 %. The model contains 306 H atoms and 50 D atoms. A total of 37 hydration water molecules were identified. The model has been refined to final agreement factors of  = 18.6 % and
= 18.6 % and 
 = 21.7 %. Several orientations of the O-D bonds of side chains, whose assignments from X-ray data were previously ambiguous, were clearly visible in the neutron structure. While most backbone N-H bonds had undergone some degree of H/D exchange throughout the molecule, five H atom positions still had distinctly negative (H) peaks. The neutron Fourier maps clearly showed the details of an extensive set of H bonds involving the ND
= 21.7 %. Several orientations of the O-D bonds of side chains, whose assignments from X-ray data were previously ambiguous, were clearly visible in the neutron structure. While most backbone N-H bonds had undergone some degree of H/D exchange throughout the molecule, five H atom positions still had distinctly negative (H) peaks. The neutron Fourier maps clearly showed the details of an extensive set of H bonds involving the ND
 terminus that may contribute to the unusual thermostability of this molecule.
terminus that may contribute to the unusual thermostability of this molecule.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri, Masaki; Aratono, Yasuyuki; Kanno, Ikuo*; Hishiki, Shigeomi*; Sugiura, Osamu*; Murase, Yasuhiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 520(1-3), p.76 - 79, 2004/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:48.81(Instruments & Instrumentation)The neutron-detection characteristics of a cryogenic neutron detector comprising an InSb semiconductor detector and a helium-3 gas converter were evaluated at a gas pressure of up to 12.5atm at 4.2K. The detector successfully detected stable neutrons under these conditions, where the density of the helium-3 gas is a few-hundred times higher than that at room temperature. It was found that the neutron detection efficiency was correlated with the gas pressure - even in a backward-detection configuration - in low-temperature, high-pressure helium-3.
 B
B O
O single-crystal absorber
single-crystal absorberNakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri, Masaki; Ukibe, Masahiro*; Ikeuchi, Takashi*; Okubo, Masataka*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 520(1-3), p.67 - 69, 2004/03
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:84.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)We succeeded in detecting neutrons using superconducting tunnel junctions (STJs) fabricated on a single crystal of Li B
B O
O . Neutrons are captured in the crystal by the nuclear reactions
. Neutrons are captured in the crystal by the nuclear reactions  Li + n
Li + n  T+
T+  + 4.78 MeV and
+ 4.78 MeV and  B + n
B + n 
 Li +
Li +  + 2.3 MeV, and generated phonons propagate in the absorber and are measured by the STJs. We selected a single crystal of Li
+ 2.3 MeV, and generated phonons propagate in the absorber and are measured by the STJs. We selected a single crystal of Li B
B O
O as the absorber material because of properties such as the large neutron cross-section of
as the absorber material because of properties such as the large neutron cross-section of  Li and
Li and  B, low
B, low  -ray sensitivity, short particle range in the substrate, and fast phonon velocity. Series-connected or multiple STJs on the crystal would enable two-dimensional neutron imaging with high detection efficiency, low gamma-ray background, and a high spatial resolution of a few microns. We demonstrate neutron detection by the STJs and show their X-ray response and neutron detection. The correlation in pulse heights between two junctions located 1.3mm apart clearly indicates the possibility of neutron imaging.
-ray sensitivity, short particle range in the substrate, and fast phonon velocity. Series-connected or multiple STJs on the crystal would enable two-dimensional neutron imaging with high detection efficiency, low gamma-ray background, and a high spatial resolution of a few microns. We demonstrate neutron detection by the STJs and show their X-ray response and neutron detection. The correlation in pulse heights between two junctions located 1.3mm apart clearly indicates the possibility of neutron imaging.
Niimura, Nobuo
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 70(Suppl.A), p.396 - 399, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Matsubayashi, Masahito; Kobayashi, Hisao*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Mishima, Kaichiro*
Nuclear Technology, 132(2), p.309 - 324, 2000/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:81.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Matsubayashi, Masahito
JAERI-Conf 99-006, p.361 - 366, 1999/08
no abstracts in English
Matsubayashi, Masahito; Hibiki, Takashi*; Mishima, Kaichiro*
Proceedings of 6th World Conference on Neutron Radiography (WCNR6), p.261 - 268, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Abe, Tetsuya; Hiroki, Seiji
FC Report, 15(12), p.276 - 278, 1997/00
no abstracts in English